Naloxone Drug Overdose Prevention
Naloxone is a medicine that rapidly reverses an opioid overdose. It is an opioid antagonist. This means that it attaches to opioid receptors and reverses and blocks the effects of other opioids. Naloxone can quickly restore normal breathing to a person if their breathing has slowed or stopped because of an opioid overdose

Naloxone is an opioid antagonist medicine used to block or turn around the impacts of opioid drugs, especially inside the setting of medication overdoses which are quickly turning into the main source of death around the world. All the more explicitly, Naloxone has a high partiality for μ-narcotic receptors, where it works as a reverse agonist, causing the quick expulsion of some other medications bound to these receptors. When opioid medication is taken in huge amounts, it can cause dangerous side effects such as respiratory depression, decreased pulse, slurred speech, tiredness, and contracted pupils. If all these symptoms are ignored and remain untreated, this can lead to vomiting, missing heartbeat and breathing, and even can lead to death. Naloxone is always referred for the fast inversion of these side effects of central nervous system depression due to opioid overdose.
When injected intravenously, Naloxone acts within 2-3 minutes. Notably, if the Naloxone injection is infused into a person who is not using any opioid medications, no effects can be seen in them. On the other side, if a person is using opioid medications and goes through opioid overdose, the Naloxone injection quickly reverses the opioid effects and can make the infused individual to promptly respond to the withdrawal indications.
Due to the short duration of medication response, people infused with Naloxone ought to be checked for responsiveness and possibly can be infused for the second time or should be taken to the clinic.
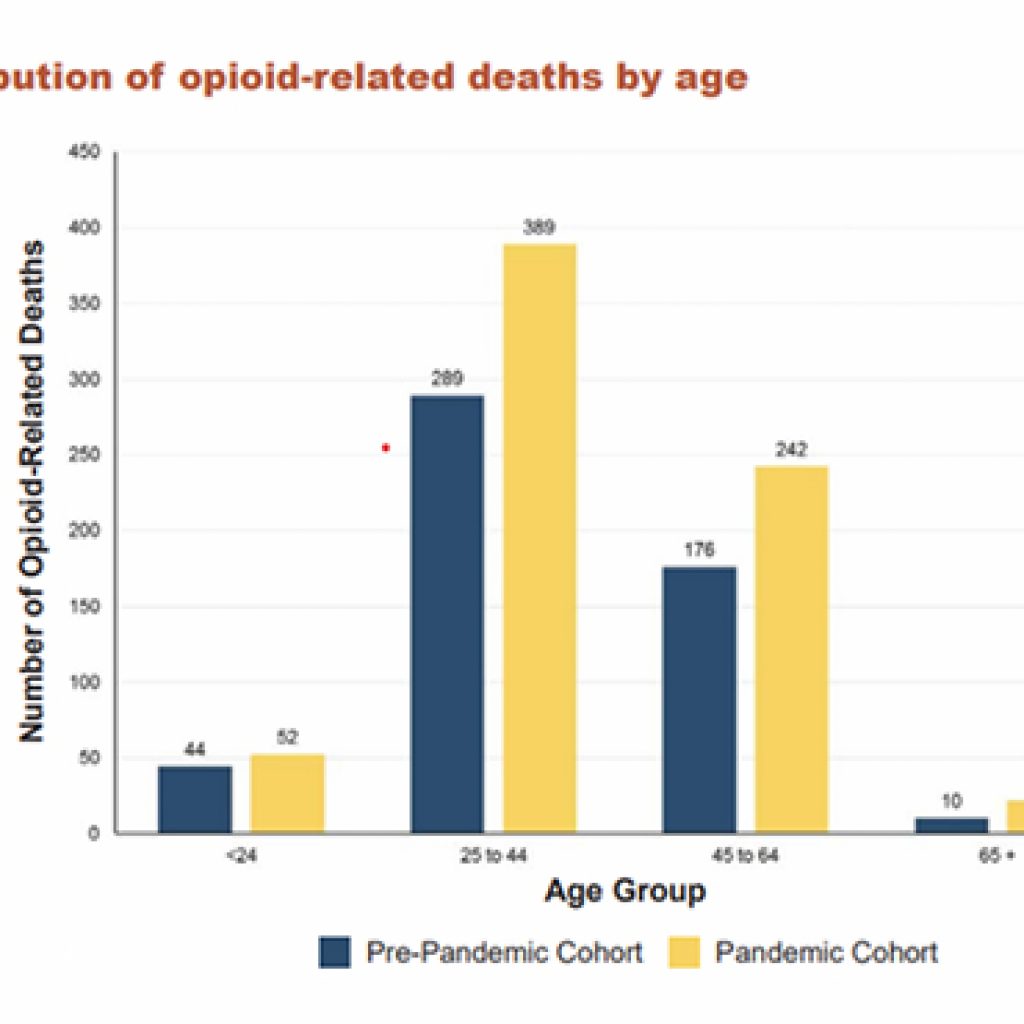
Some Sad Facts
More than 12,800 apparent opioid-related deaths occurred between Jan 2016 and March 2019.